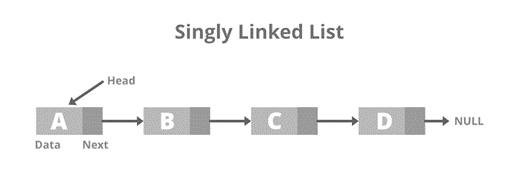
6.DELETE FROM ANY POSITION
- Validate the position.
- Check if the list is empty.
- If deleting the first node, handle separately.
- Traverse to the node at the given position.
- Update the previous node’s next to the current node’s next.
- Update the next node’s prev to the current node’s prev.
- Free the current node.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ARRAY AND LINKED LIST
| ARRAY | LINKED LIST |
| Array is a collection of homogeneous (similar) datatype. | Linked list is a collection of nodes |
| Array elements are stored in continuous memory locations | Linked list elements can be stored anywhere in the memory. |
| Array work with static data structures. | Linked list works with dynamic data structure. |
| Array elements are independent. | Linked list elements are dependent to each other. |
Source link
4.DELETE FROM THE BEGINNING
- Check if the list is empty.
- If there’s only one node, free it and set the head to NULL.
- If the list has more than one node, find the last node.
- Set the last node’s next to the second node.
- Update the second node’s prev to the last node.
- Free the head node.
- Update the head to point to the second node.
5.DELETE FROM THE END
- Check if the list is empty.
- If there’s only one node, free it and set the head to NULL.
- If the list has more than one node, traverse to the second last node.
- Set the second last node’s next to the head.
- Update the head’s prev to the second last node.
- Free the last node.
6.DELETE FROM ANY POSITION
- Validate the position.
- Check if the list is empty.
- If deleting the first node, handle separately.
- Traverse to the node at the given position.
- Update the previous node’s next to the current node’s next.
- Update the next node’s prev to the current node’s prev.
- Free the current node.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ARRAY AND LINKED LIST
| ARRAY | LINKED LIST |
| Array is a collection of homogeneous (similar) datatype. | Linked list is a collection of nodes |
| Array elements are stored in continuous memory locations | Linked list elements can be stored anywhere in the memory. |
| Array work with static data structures. | Linked list works with dynamic data structure. |
| Array elements are independent. | Linked list elements are dependent to each other. |
Source link
3.INSERT AN ITEM AT ANY POSITION
- Validate the position.
- Create a new node.
- Assign the new node’s data to the given value.
- If inserting at the beginning, update the head and return.
- Traverse to the node before the desired position.
- Update the new node’s next to the current node’s next.
- Update the current node’s next to the new node.
4.DELETE FROM THE BEGINNING
- Check if the list is empty.
- If there’s only one node, free it and set the head to NULL.
- If the list has more than one node, find the last node.
- Set the last node’s next to the second node.
- Update the second node’s prev to the last node.
- Free the head node.
- Update the head to point to the second node.
5.DELETE FROM THE END
- Check if the list is empty.
- If there’s only one node, free it and set the head to NULL.
- If the list has more than one node, traverse to the second last node.
- Set the second last node’s next to the head.
- Update the head’s prev to the second last node.
- Free the last node.
6.DELETE FROM ANY POSITION
- Validate the position.
- Check if the list is empty.
- If deleting the first node, handle separately.
- Traverse to the node at the given position.
- Update the previous node’s next to the current node’s next.
- Update the next node’s prev to the current node’s prev.
- Free the current node.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ARRAY AND LINKED LIST
| ARRAY | LINKED LIST |
| Array is a collection of homogeneous (similar) datatype. | Linked list is a collection of nodes |
| Array elements are stored in continuous memory locations | Linked list elements can be stored anywhere in the memory. |
| Array work with static data structures. | Linked list works with dynamic data structure. |
| Array elements are independent. | Linked list elements are dependent to each other. |